MIL-PRF-123D
d. Capacitance.
e. Dissipation factor.
The manufacturer has the option of performing these electrical tests in any order except insulation resistance shall
always be done after dielectric withstanding voltage. If the voltage conditioning test is performed with individual
fuses in series with each part, any part tested in a position where a fuse fails shall be tested for insulation resistance
and dielectric withstanding voltage. If the part meets the initial requirements for insulation resistance and dielectric
withstanding voltage, the part shall be rejected but shall not count against the PDA in table XVI. The manufacturer
also has the option to not test parts with fuse failures and count these toward the PDA.
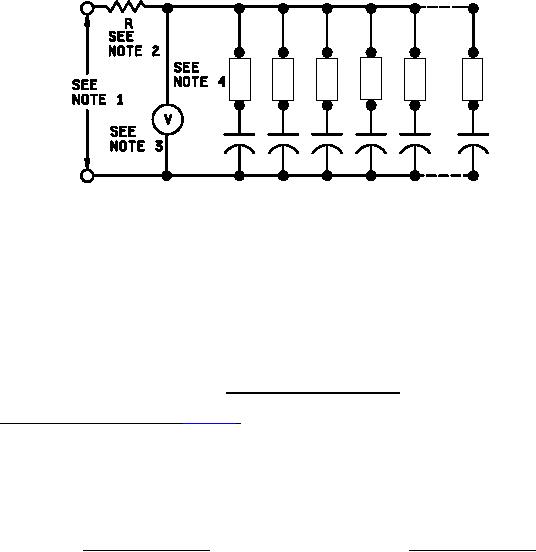
NOTES:
*
1. The power supply shall be capable of supplying the required test voltage.
2. The current limiting device shall be a resistor and/or a fuse. The current shall be limited to no less than 30
milliamperes (mA) and no more than 10 A.
3. There shall be a voltage monitor that will trigger an alarm and shut off the test if the applied voltage drops
by more than 5 percent.
*
4. Fuses and resistors are optional. The value of the resistors and fuses shall be such that they do not
restrict the power supply's ability to provide the required test voltage to the device under test (±5 percent).
5. The capacitor bank shall be no less than 10 capacitors.
*
FIGURE 4. Voltage conditioning circuitry.
4.6.6.2.2 Optional voltage conditioning (see 3.10). The manufacturer, with approval from the qualifying activity,
may perform an optional voltage conditioning test instead of the standard voltage conditioning test of 4.6.6.2.1. All
conditions of 4.6.6.2.1 apply, with the exception of the voltage applied, the test time, and the time required for
meeting the PDA. The accelerated condition selected for the optional voltage conditioning shall be used for the
duration of the test. At no time shall a combination of standard and optional voltage conditioning be allowed on the
same samples. The minimum time duration, T(test) minimum, and the time required for meeting the PDA, T(test)
PDA, shall be calculated as follows:
1344
384
=
=
Ttest (min .)
Ttest (PDA)
3
3
(E test / Erated )
(E test / Erated )
2 x Erated ≤ Etest ≤ 4 x Erated
Where:
= Applied voltage
Etest
= Rated voltage of the capacitor
Erated
Ttest (min.) = Minimum test time in hours
Ttest (PDA) = Time required for meeting the PDA
21
For Parts Inquires submit RFQ to Parts Hangar, Inc.
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business