MIL-PRF-123D
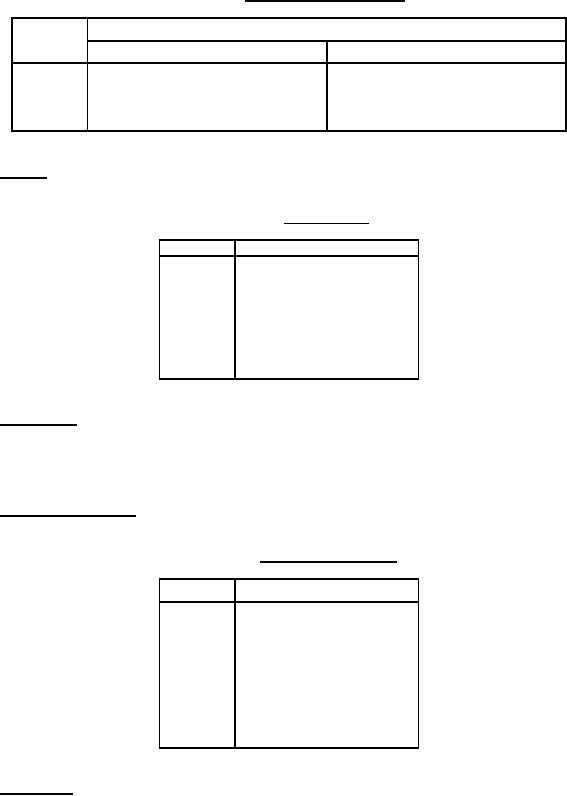
TABLE I. Voltage-temperature limits.
Capacitance change with reference to +25°C
Symbol
Steps A through D of table XVIII
Steps E through G of table XVIII
90 ±20 ppm/°C
90 ±20 ppm/°C
G
0 ±30 ppm/°C
0 ±30 ppm/°C
P
R
+15, -40 percent
+15, -15 percent
X
+15, -25 percent
+15, -15 percent
1.2.1.3 Voltage. The rated voltage for continuous operation at +125°C is identified by a single letter as shown in
table II.
TABLE II. Rated voltage.
Symbol
Rated voltage (Volts, dc)
A
25
B
50
C
100
D
200
E
500
K
150
L
300
M
400
1.2.1.4 Capacitance. The nominal capacitance value, expressed in picofarads (pF) is identified by a three digit
number; the first two digits represent significant figures and the last digit specifies the number of zeros to follow.
When the nominal value is less than 10 pF, the letter "R" is used to indicate the decimal point and the succeeding
digit(s) of the group represent significant figure(s). 1R0 indicates 1.0 pF; R75 indicates .75 pF; and 0R5 indicates
0.5 pF.
1.2.1.5 Capacitance tolerance. The capacitance tolerance is identified by a single letter as shown in table III.
TABLE III. Capacitance tolerance.
Capacitance tolerance ±
Symbol
B
0.1 pF
C
0.25 pF
D
0.5 pF
F
1 percent
G
2 percent
J
5 percent
K
10 percent
M
20 percent
1.2.1.6 Termination. The termination is identified by a single letter as shown in table IV. Nonleaded termination
types W and Y are no longer available. Nonleaded termination W (100 percent tin or tin-lead alloy) and nonleaded
termination Y (100 percent tin) were removed due to the possibility of tin whisker growth. Termination Z is a direct
replacement. Termination S may also be suitable, but since solder coating increases the length, width, and height
(see 3.1), the user should determine if capacitors will fit into their design. Leaded termination A (copper-iron-zinc
(194 alloy)) is no longer available.
2
For Parts Inquires submit RFQ to Parts Hangar, Inc.
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business